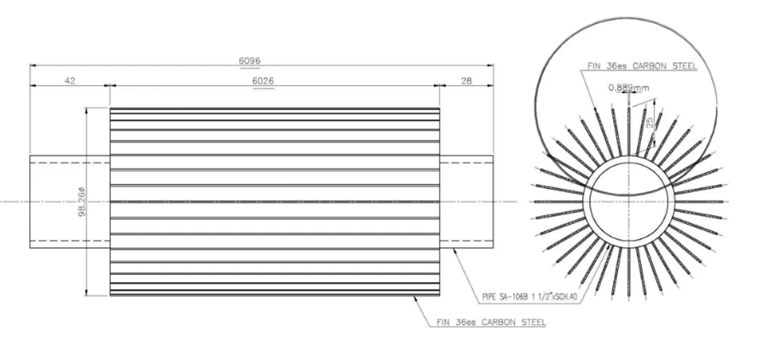
Longitudinal Finned Tube for Heat Exchanger
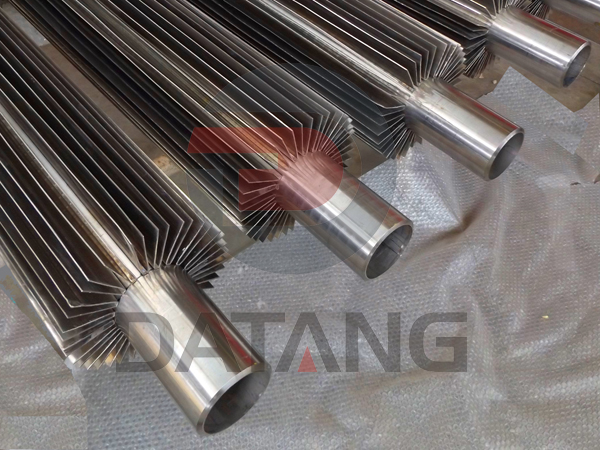
Longitudinal fin tube is an efficient heat transfer element, and its structural characteristics play a vital role in the heat exchange process. This tube type significantly increases the heat transfer area, allowing heat to be transferred faster and more evenly, thus having higher heat transfer efficiency than traditional finless tubes under the same conditions.
Setting position: According to the fin setting position,longitudinal fin tubes can be divided into outer fin tubes,inner fin tubes,and both internal and external types. Outer finned tube means that the fins are set outside the tube, and inner finned tube means that the fins are set inside the tube.
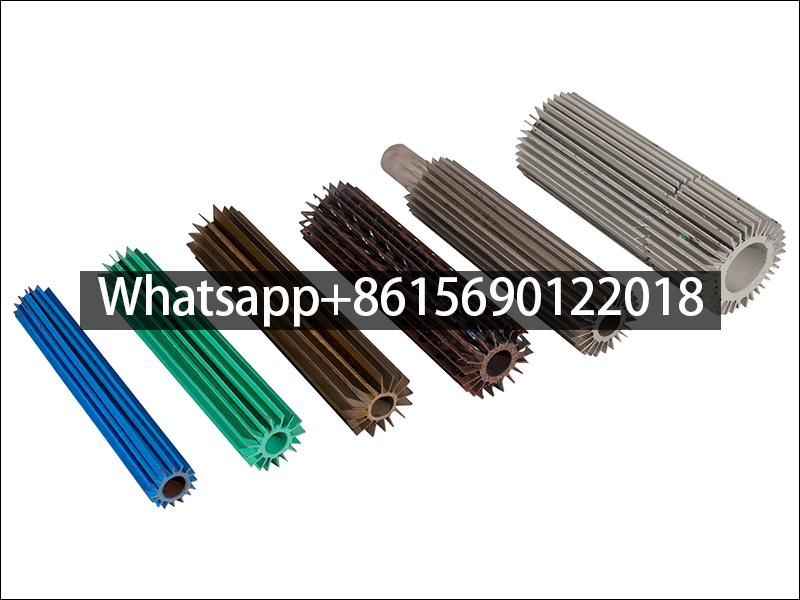
Longitudinal Finned Tubes by Material
Longitudinal finned tubes can be classified according to their structural type, fin shape, setting position and manufacturing process.
Structural type: Longitudinal finned tubes can be divided into two basic types: longitudinal and radial. The design of finned tubes with large helix angle is closer to the longitudinal structure, while the finned tube with small helix angle is closer to the radial structure.
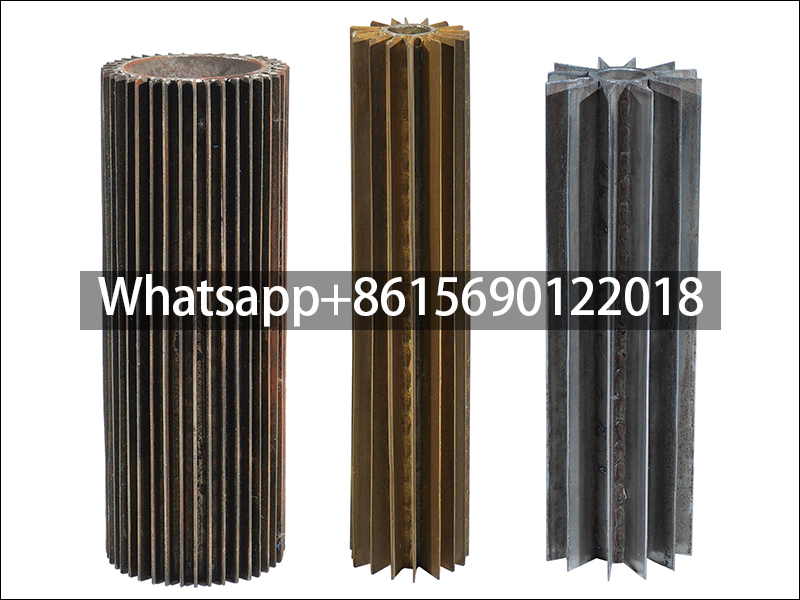
Fin shape: There are many choices for fin shapes, including circular, rectangular, and needle-shaped. The choice of these shapes usually depends on the specific application needs and heat transfer efficiency.
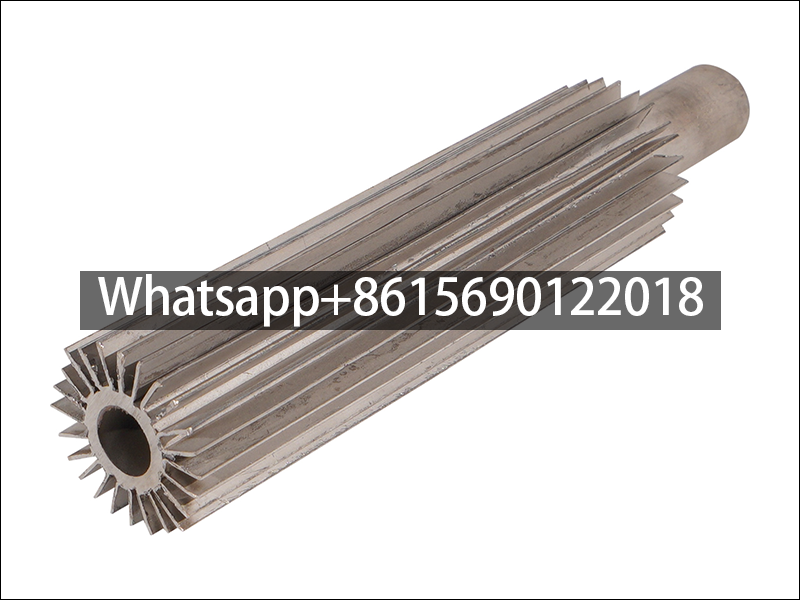
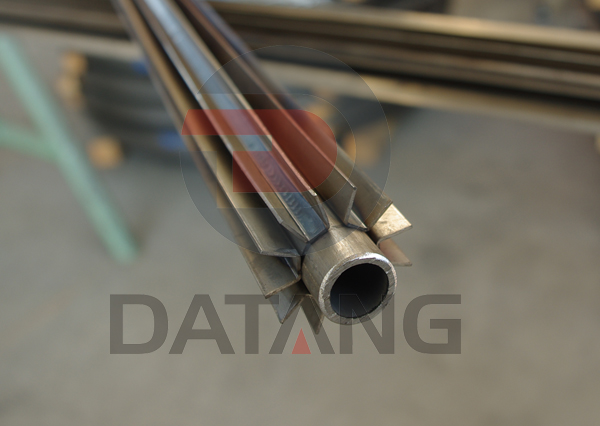
Manufacturing process: From the perspective of manufacturing process, longitudinal fin tubes can be divided into various types such as integral fin tubes, welded fin tubes, high-frequency welded fin tubes and mechanically connected fin tubes. Integral finned tubes are made of casting, machining or rolling, the fins and the tube are integrated.
Welded fin tubes are manufactured using processes such as brazing or inert gas shielded welding, and the fins and tubes are connected by welding. High-frequency welding finned tubes use the high-frequency electric induction generated by the high-frequency generator to generate high temperature at the contact point between the surface of the tube and the fins, and then melt the two within a small depth range, and then pressurize the fins Integrated with the pipe. Mechanically connected finned tubes mechanically connect the fins and tubes together, can be disassembled and replaced according to actual needs, and maintained easily.
These classifications provide a variety of options to select the most suitable longitudinal fin tube type based on factors such as specific heat transfer needs, working environment and cost requirements.
The design of the longitudinal fin tube not only improves the heat transfer efficiency, but also has the characteristics of compact structure, which reduces the volume of the entire heat exchanger and saves space. This characteristic makes longitudinal finned tubes have broad application prospects in situations where space is limited, such as aerospace, automobiles, electronic equipment and other fields.
Longitudinal finned tubes also have good mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. The connection between the fins and the base tube is strong and able to withstand high operating pressure and temperature fluctuations. At the same time, the selection of fin materials also has high flexibility. Different corrosion-resistant materials can be selected according to the specific working environment and usage requirements to extend the service life of the longitudinal fin tubes. In addition, Longitudinal finned tubes are easy to process and install. The fins can be closely combined with the base tube through stamping, welding, etc. to form an integrated heat transfer element. During the installation process, the longitudinal finned tubes can be cut, bent, etc. as needed to adapt to various complex installation environments.
In summary, longitudinal fin tubes, with their unique structural characteristics and excellent performance, have shown significant advantages in the field of heat exchange and have become the preferred heat transfer element in many application fields.