Types of Corrosion in Air-Cooler Tube Bundles and Their Protection Strategies
01.Overview of Corrosion in Air-Cooler Tube Bundles
Air-coolers are crucial equipment in the petrochemical industry, operating in high-temperature, high-pressure, and corrosive environments. As the core component of the air-cooler, the corrosion of the tube bundle directly impacts the equipment’s operational safety and lifespan.
Understanding different corrosion types and implementing targeted protective measures is essential. Analyzing and implementing effective protection strategies can extend equipment lifespan and ensure production continuity and safety.

► Corrosion Classification and Protection Strategies
Different corrosion types have varying impacts on equipment; therefore, different protection strategies are required. These strategies not only help extend equipment lifespan but also effectively improve overall operational safety.
02 Corrosion Type Analysis
► Pitting Corrosion
Pitting corrosion is prone to occur in media containing high dissolved oxygen and harmful anions (especially Cl ions). This corrosion typically develops in small areas of the tube bundle, gradually eroding the interior and eventually causing pitting corrosion. Severe pitting corrosion can lead to equipment perforation. The main factors affecting pitting corrosion include heat treatment aging temperature and material surface finish.

► Crack Corrosion
Crack corrosion occurs due to the retention of media within tiny gaps. Common locations include joints and connections. In air-cooled heat exchangers, the gap between the base tube and the liner is particularly common. Such gaps can be effectively eliminated through design optimization, such as full expansion joints.
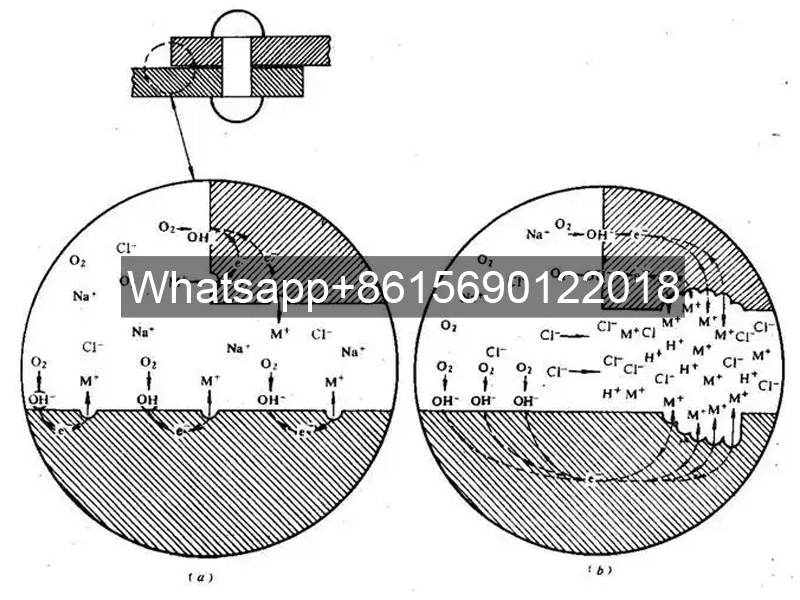
► Intergranular Corrosion and Stress Corrosion
Intergranular corrosion is caused by the uneven chemical composition of alloy materials and the action of corrosive media. Stress corrosion refers to the fracture of materials under stress and the combined action of a corrosive environment. In air coolers, hydrogen sulfide stress corrosion cracking is particularly prominent and requires special attention.

03 Corrosion Rate Testing
► Resistance Method and Linear Polarization Method
The resistance method is an effective method for monitoring corrosion conditions, continuously monitoring the corrosion of air cooler tube bundles. The linear polarization method, due to its high sensitivity, is suitable for determining instantaneous corrosion rates. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages and are suitable for different situations.
► Weight Loss Method
The weight loss method is a simple and effective method for determining corrosion rates. The corrosion rate can be easily and accurately measured using the plate-mounted corrosion test, which is a commonly used experimental method.
04 Corrosion Protection Measures
► Material Selection and Design
Selecting suitable materials is crucial for corrosion protection. The selected materials must possess corrosion resistance and other physical properties compatible with the operating environment, while also meeting requirements for mechanical properties such as strength and hardness.
► Manufacturing Process Optimization
During the manufacturing process, controlling stress and optimizing heat treatment can reduce the risk of corrosion. Adopting appropriate process measures can improve the corrosion resistance of materials and avoid potential risks caused by improper processing.
Through in-depth analysis and scientific protection, the safety and lifespan of air cooler tube bundles can be effectively improved, which is crucial for the continuous and stable operation of petrochemical plants.






