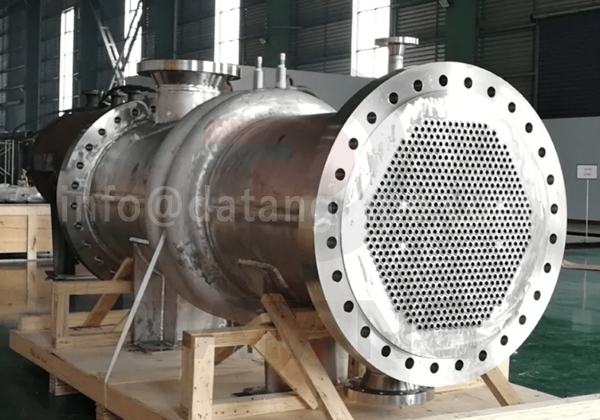
The concept and operation of a shell and tube heat exchanger are rather simple and are based on the flow and thermal contact of two liquids. The name of a shell and tube heat exchanger serves as an explanation of the process, which is the exchanging of temperature between two fluids. In a heat exchanger, a heated or hot fluid will flow around a cold fluid and transfer heat in the direction of the flow of the cold fluid.

Shell and tube heat exchangers
In any situation where two pieces of material make contact, there will be an exchange or transfer of heat through a conductive surface. The process of a shell and tube heat exchanger provides a place for two fluids to exchange or transfer heat through conductive metals.
Tube sheet
In the shell and tube heat exchanger process, one fluid flows through the tubes while the other fluid flows through the shell. In the diagram below, which is of a straight tube shell and tube heat exchanger, the shell inlet for the shell fluid to enter is at the top with the inlet for the tube fluid at the bottom right.

Tube Sheets
A shell and tube heat exchanger has two compartments or sections: the shell side and the tube side. When working with a shell and tube heat exchanger, it is important to decide on which side the hot fluid will enter and on which the cold fluid will enter; this decision is referred to as fluid allocation.
When there is a difference in pressure between the fluids, the lower pressure fluid enters through the shell inlet since the tubes are designed to handle high pressure.






