What is an economizer and How Can it Benefit Commercial HVAC Unit?
What is an economizer and How Can it Benefit Commercial HVAC Unit?
Economizer is a device installed at the bottom of the flue at the tail of the boiler to recover the waste heat of the exhaust gas. It heats the boiler feed water into a saturated water heating surface under the drum pressure. Because it absorbs the heat of high-temperature flue gas, it reduces the exhaust temperature of the flue gas, saves energy and improves efficiency, so it is called an economizer.
Name:Economizer
Type:Energy-saving
Outer diameter:32~51mm
Pipe material:Carbon steel pipe
Common name:Snake pipe
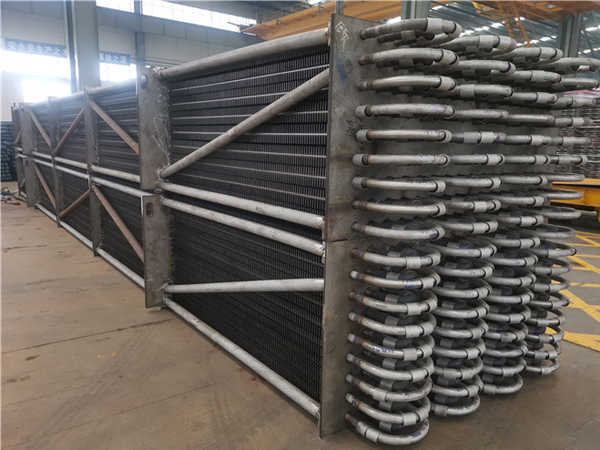

What is an economizer and How Can it Benefit Commercial HVAC Unit
Steel tube economizer is not limited by pressure and can be used as a boiling type. It is generally made of carbon steel pipes with an outer diameter of 32 to 51 mm. Sometimes fins and ribs are added to the outside of the tube to improve the heat transfer effect. The steel tube economizer consists of horizontally arranged parallel elbow pipes (commonly known as serpentine pipes).
Economizers are mainly suitable for industry, and are gradually popularized in agriculture and some related industries and commerce.
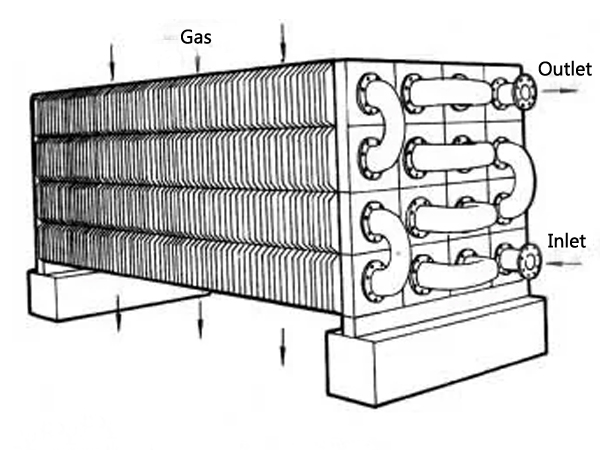
Power plant industrial boiler economizer
Economizer classification
There are many ways to classify economizers, which can be classified according to the following methods:
- According to the degree of heating of the feed water: it can be divided into non-boiling type and boiling type.
- According to the manufacturing material: there are two types of cast iron and steel tube economizers. Non-boiling economizers are mostly made of cast iron, but some are made of steel pipes, while boiling economizers can only be made of steel pipes. Cast iron economizers are mostly used in boilers with pressures ≤ 2.5MPa. If the pressure exceeds 2.5MPa, economizers made of steel pipes should be used.
- According to the form of the device: there are two types: vertical and horizontal.
- According to the relative flow direction of exhaust gas and feed water: there are three types: downstream, countercurrent and mixed.
- According to the structural form: light tube economizer and fin economizer. Fin economizers include: H-type economizer (more commonly used) and spiral fin economizer.
- According to the form of heat conduction: direct conduction and indirect conduction;
Direct conduction is to use boiler tail gas to directly radiate and preheat boiler water; indirect conduction is to indirectly preheat boiler water through a heat transfer medium.
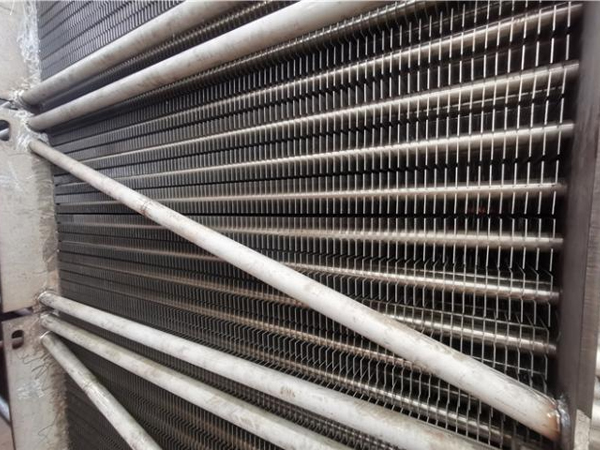

Heat exchanger Inside the economizer-datang fin tube
Function of economizer
- Absorb the heat of low-temperature flue gas, reduce the exhaust temperature, reduce exhaust loss, and save fuel.
- Since the feed water is heated in the economizer before entering the drum, the heat absorption of the feed water on the heating surface is reduced, and the economizer can be used to replace part of the evaporation heating surface with a higher cost.
- When the feed water temperature is increased, the wall temperature difference will be reduced when entering the drum, and the thermal stress will be reduced accordingly, extending the service life of the drum.
Energy-saving principle of economizer
Add a heat recovery process to the cycle. Increase the average heat absorption temperature. Thereby increasing the cycle efficiency.
During the startup process of the boiler (drum boiler), since the circulation of its steam-water pipeline is not established, that is, the boiler feed water is in a stagnant state, the water in the economizer is in a non-flowing state.
With the strengthening of boiler combustion and the increase of flue gas temperature, the water in the economizer is easy to vaporize, causing the economizer to be partially in an over-temperature state. In order to avoid this situation, a pipe is connected from the centralized downpipe of the drum to the inlet of the economizer as a recirculation pipe to keep the water in the economizer in a flowing state to avoid its vaporization.
Boiler economizer failure inspection and maintenance
The main cause of large-capacity boiler economizer failure is leakage of the serpentine tube. Most leakages are caused by the following three reasons:
(1) tube wall wear
(2) poor welding quality
(3) inner wall corrosion.
In a few cases, there are other reasons, such as poor tube material, cracks in the tube wall in the heat affected zone of the weld, etc. The inspection and maintenance work should aim to eliminate these factors, master the internal laws, and take preventive measures.






